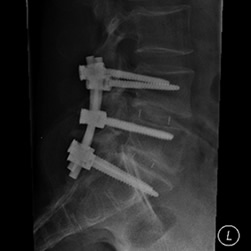
 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MIS)
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MIS)
MIS is used to treat disorders of the spine with less disruption to the muscles. This can result in quicker recovery, decrease operative blood loss, and speed patient return to normal function.
Not all patients are appropriate candidates for MIS procedures. It is important to keep in mind that there needs to be certainty that the same or better results can be achieved through MIS techniques as with the respective open procedure.
Disadvantage of Conventional Open Lumbar Spine Surgery
- Larger incision.
- Damage to normal tissue: the muscle dissection and retraction required to uncover the spine (which contributes to the formation of scar and fibrotic tissue).
- The need for blood vessel cauterization, and the necessity of bone removal.
- Disrupting natural spinal anatomy is necessary to facilitate decompression of pinched nerves and the placement of screws and devices to stabilize the spine.
- This may lead to lengthy hospital stays, prolonged pain and recovery periods, the need for postoperative narcotic use, significant operative blood loss, and risk of tissue infection.
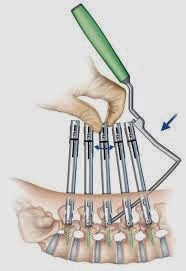
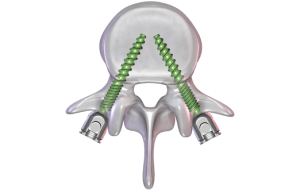 Advantages of MIS
Advantages of MIS
- Smaller incisions.
- Smaller scars/less scar tissue.
- Reduced blood loss.
- Less pain.
- Less soft tissue damage.
- Reduced muscle retraction.
- Decreased postoperative narcotics.
- Shorter hospital stay.
- Possibility of performing on outpatient basis.
- Faster recovery.
- Quicker return to work and activities.